Broker Balancers
Apache ActiveMQ Artemis broker balancers allow incoming client connections to be distributed across multiple target brokers. The target brokers are grouped in pools and the broker balancers use a target key to select a target broker from a pool of brokers according to a policy.
This feature is still EXPERIMENTAL and not meant to be run in production yet. Furthermore, its configuration can change until declared as officially stable.
Target Broker
Target broker is a broker that can accept incoming client connections and is local or remote. The local target is a special target that represents the same broker hosting the broker balancer. The remote target is another reachable broker.
Target Key
The broker balancer uses a target key to select a target broker. It is a string retrieved from an incoming client connection, the supported values are:
CLIENT_IDis the JMS client ID.SNI_HOSTis the hostname indicated by the client in the SNI extension of the TLS protocol.SOURCE_IPis the source IP address of the client.USER_NAMEis the username indicated by the client.ROLE_NAMEis a role associated with the authenticated user of the connection.
Pools
The pool is a group of target brokers with periodic checks on their state.
It provides a list of ready target brokers to distribute incoming client connections only when it is active.
A pool becomes active when the minimum number of target brokers, as defined by the quorum-size parameter, become ready.
When it is not active, it doesn't provide any target avoiding weird distribution at startup or after a restart.
Including the local broker in the target pool allows broker hosting the balancer to accept incoming client connections as well.
By default, a pool doesn't include the local broker, to include it as a target the local-target-enabled parameter must be true.
There are three pool types: cluster pool, discovery pool and static pool.
Cluster Pool
The cluster pool uses a cluster connection to get the target brokers to add. Let's take a look at a cluster pool example from broker.xml that uses a cluster connection:
<pool>
<cluster-connection>cluster1</cluster-connection>
</pool>
Discovery Pool
The discovery pool uses a discovery group to discover the target brokers to add. Let's take a look at a discovery pool example from broker.xml that uses a discovery group:
<pool>
<discovery-group-ref discovery-group-name="dg1"/>
</pool>
Static Pool
The static pool uses a list of static connectors to define the target brokers to add. Let's take a look at a static pool example from broker.xml that uses a list of static connectors:
<pool>
<static-connectors>
<connector-ref>connector1</connector-ref>
<connector-ref>connector2</connector-ref>
<connector-ref>connector3</connector-ref>
</static-connectors>
</pool>
Defining pools
A pool is defined by the pool element that includes the following items:
- the
usernameelement defines the username to connect to the target broker; - the
passwordelement defines the password to connect to the target broker; - the
check-periodelement defines how often to check the target broker, measured in milliseconds, default is5000; - the
quorum-sizeelement defines the minimum number of ready targets to activate the pool, default is1; - the
quorum-timeoutelement defines the timeout to get the minimum number of ready targets, measured in milliseconds, default is3000; - the
local-target-enabledelement defines whether the pool has to include a local target, default isfalse; - the
cluster-connectionelement defines the cluster connection used by the cluster pool. - the
static-connectorselement defines a list of static connectors used by the static pool; - the
discovery-groupelement defines the discovery group used by the discovery pool.
Let's take a look at a pool example from broker.xml:
<pool>
<quorum-size>2</quorum-size>
<check-period>1000</check-period>
<local-target-enabled>true</local-target-enabled>
<static-connectors>
<connector-ref>connector1</connector-ref>
<connector-ref>connector2</connector-ref>
<connector-ref>connector3</connector-ref>
</static-connectors>
</pool>
Policies
The policy define how to select a broker from a pool. The included policies are:
FIRST_ELEMENTto select the first target broker from the pool which is ready. It is useful to select the ready target brokers according to the priority defined with their sequence order, ie supposing there are 2 target brokers this policy selects the second target broker only when the first target broker isn't ready.ROUND_ROBINto select a target sequentially from a pool, this policy is useful to evenly distribute;CONSISTENT_HASHto select a target by a key. This policy always selects the same target broker for the same key until it is removed from the pool.LEAST_CONNECTIONSto select the targets with the fewest active connections. This policy helps you maintain an equal distribution of active connections with the target brokers.
A policy is defined by the policy element. Let's take a look at a policy example from broker.xml:
<policy name="FIRST_ELEMENT"/>
Cache
The broker balancer provides a cache with a timeout to improve the stickiness of the target broker selected,
returning the same target broker for a target key as long as it is present in the cache and is ready.
So a broker balancer with the cache enabled doesn't strictly follow the configured policy.
By default, the cache is enabled and will never timeout. See below
for more details about setting the cache-timeout parameter.
Key transformers
A local-target-key-transformer allows target key transformation before matching against any local-target-filter. One use case is
CLIENT_ID sharding across a cluster of N brokers. With a consistent hash % N transformation, each client id
can map exclusively to just one of the brokers. The included transformers are:
CONSISTENT_HASH_MODULOthat takes a singlemoduloproperty to configure the bound.
Defining broker balancers
A broker balancer is defined by the broker-balancer element, it includes the following items:
- the
nameattribute defines the name of the broker balancer and is used to reference the balancer from an acceptor; - the
target-keyelement defines what key to select a target broker, the supported values are:CLIENT_ID,SNI_HOST,SOURCE_IP,USER_NAME,ROLE_NAME, default isSOURCE_IP, see target key for further details; - the
target-key-filterelement defines a regular expression to filter the resolved keys; - the
local-target-filterelement defines a regular expression to match the keys that have to return a local target; - the
local-target-key-transformerelement defines a key transformer, see key transformers; - the
cache-timeoutelement is the time period for a target broker to remain in the cache, measured in milliseconds, setting0will disable the cache, default is-1, meaning no expiration; - the
poolelement defines the pool to group the target brokers, see pools. - the
policyelement defines the policy used to select the target brokers from the pool, see policies;
Let's take a look at some broker balancer examples from broker.xml:
<broker-balancers>
<broker-balancer name="local-partition">
<target-key>CLIENT_ID</target-key>
<target-key-filter>^.{3}</target-key-filter>
<local-target-filter>^FOO.*</local-target-filter>
</broker-balancer>
<broker-balancer name="simple-balancer">
<policy name="FIRST_ELEMENT"/>
<pool>
<static-connectors>
<connector-ref>connector1</connector-ref>
<connector-ref>connector2</connector-ref>
<connector-ref>connector3</connector-ref>
</static-connectors>
</pool>
</broker-balancer>
<broker-balancer name="consistent-hash-balancer">
<target-key>USER_NAME</target-key>
<local-target-filter>admin</local-target-filter>
<policy name="CONSISTENT_HASH"/>
<pool>
<local-target-enabled>true</local-target-enabled>
<discovery-group-ref discovery-group-name="dg1"/>
</pool>
<policy name="CONSISTENT_HASH"/>
</broker-balancer>
<broker-balancer name="evenly-balancer">
<target-key>CLIENT_ID</target-key>
<target-key-filter>^.{3}</target-key-filter>
<policy name="LEAST_CONNECTIONS"/>
<pool>
<username>guest</username>
<password>guest</password>
<discovery-group-ref discovery-group-name="dg2"/>
</pool>
</broker-balancer>
</broker-balancers>
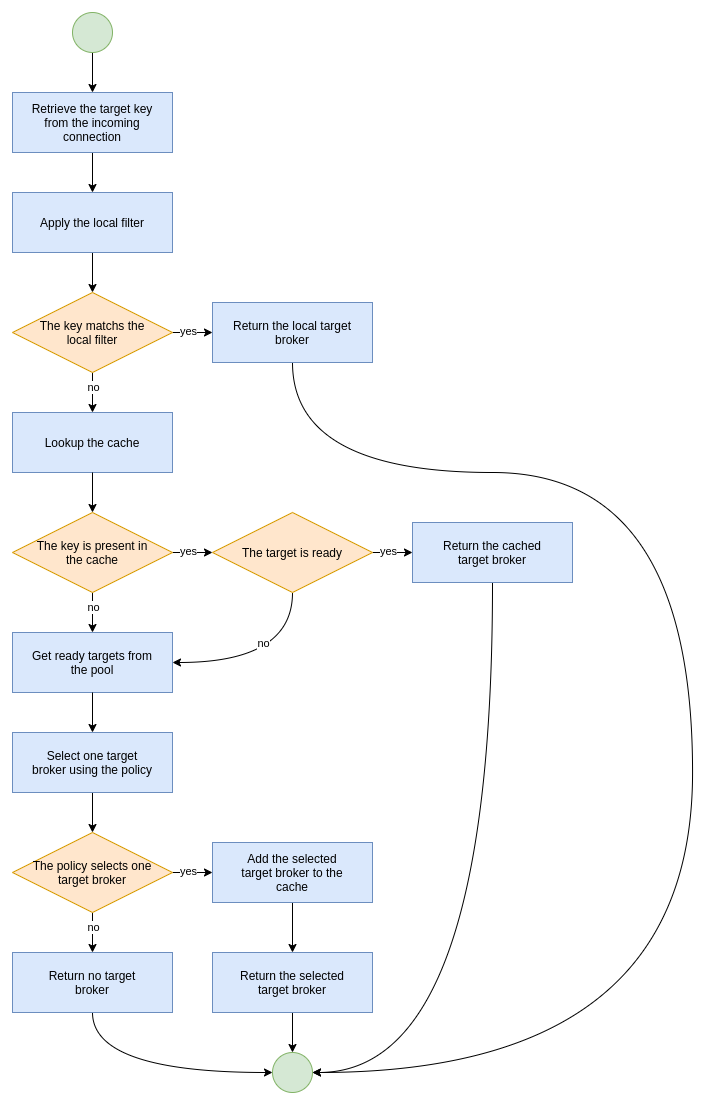
Broker Balancer Workflow
The broker balancer workflow include the following steps:
- Retrieve the target key from the incoming connection;
- Return the local target broker if the target key matches the local filter;
- Delegate to the pool:
- Return the cached target broker if it is ready;
- Get ready/active target brokers from the pool;
- Select one target broker using the policy;
- Add the selected broker in the cache;
- Return the selected broker.
Let's take a look at flowchart of the broker balancer workflow:
Data gravity
The first balancer configuration: local-partition, demonstrates the simplest use case,
that of preserving data gravity by confining a subset of application data to a given broker.
Each broker is given a subset of keys that it will exclusively service or reject.
If brokers are behind a round-robin load-balancer or have full knowledge of the broker
urls, their broker will eventually respond. The local-target-filter regular expression
determines the granularity of partition that is best for preserving data gravity for your applications.
The challenge is in providing a consistent key in all related application connections.
Note: the concept of data gravity tries to capture the reality that while addresses are shared by multiple
applications, it is best to keep related addresses and their data co-located on a single broker. Typically,
applications should connect to the data rather than the data moving to whatever broker the application connects too.
This is particularly true when the amount of data (backlog) is large, the cost of movement to follow consumers outweighs
the cost of delivery to the application.
With the 'data gravity' mindset, operators are less concerned with numbers of connections and more concerned with
applications and the addresses they need to interact with.
Redirection
Apache ActiveMQ Artemis provides a native redirection for supported clients and a new management API for other clients.
The native redirection can be enabled per acceptor and is supported only for AMQP, CORE and OPENWIRE clients.
The acceptor with the redirect-to url parameter will redirect the incoming connections.
The redirect-to url parameter specifies the name of the broker balancer to use,
ie the following acceptor will redirect the incoming CORE client connections using the broker balancer with the name simple-balancer:
<acceptor name="artemis">tcp://0.0.0.0:61616?redirect-to=simple-balancer;protocols=CORE</acceptor>
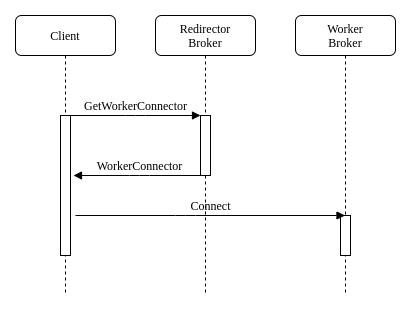
Native Redirect Sequence
The clients supporting the native redirection connect to the acceptor with the redirection enabled. The acceptor sends to the client the target broker to redirect if it is ready and closes the connection. The client connects to the target broker if it has received one before getting disconnected otherwise it connected again to the acceptor with the redirection enabled.
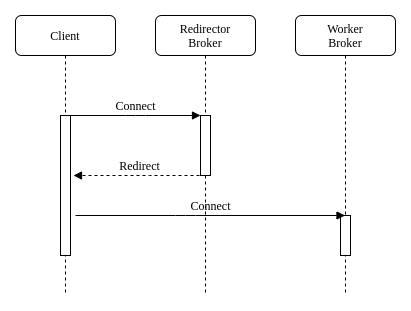
Management API Redirect Sequence
The clients not supporting the native redirection queries the management API of broker balancer to get the target broker to redirect. If the API returns a target broker the client connects to it otherwise the client queries again the API.